Or try one of the following: 詹姆斯.com, adult swim, Afterdawn, Ajaxian, Andy Budd, Ask a Ninja, AtomEnabled.org, BBC News, BBC Arabic, BBC China, BBC Russia, Brent Simmons, Channel Frederator, CNN, Digg, Diggnation, Flickr, Google News, Google Video, Harvard Law, Hebrew Language, InfoWorld, iTunes, Japanese Language, Korean Language, mir.aculo.us, Movie Trailers, Newspond, Nick Bradbury, OK/Cancel, OS News, Phil Ringnalda, Photoshop Videocast, reddit, Romanian Language, Russian Language, Ryan Parman, Traditional Chinese Language, Technorati, Tim Bray, TUAW, TVgasm, UNEASYsilence, Web 2.0 Show, Windows Vista Blog, XKCD, Yahoo! News, You Tube, Zeldman
OJ Health and Safety
Health and Safety Training, Consultancy & AssessmentH&S Compliance In The Workplace 1 Jul 2025, 10:55 am
When it comes to workplace safety, health and safety compliance isn’t just a legal box to tick — it’s your duty as an employer. Creating a safe, supportive, and hazard-free environment protects your team and strengthens your business. This then helps with compliance in the workplace.
Let’s break down what health and safety compliance really means and how you can meet your employer duties with confidence.
Why Health and Safety Compliance Matters
No one wants accidents at work. They’re costly, stressful, and often avoidable. As an employer, it’s your duty to prevent harm where you can. This doesn’t need to be complicated — just thoughtful and proactive.
By following a clear safety plan and carrying out regular health and safety risk assessments, you’ll be protecting your people and your reputation.
Understanding Employer Duties
All employers in the UK have legal responsibilities. These employer duties are in place to keep workers safe, both physically and mentally. You must take steps to identify risks, put controls in place, and review them often.
A key part of this is conducting regular health and safety risk assessments. These highlight hazards in the workplace and help you decide what action is needed.
Tip: Schedule reviews of your risk assessments every six months, or after any major change in the workplace.
The Role of Health and Safety Risk Assessments
Health and safety risk assessments are at the heart of compliance. They help you spot issues before they become incidents. Start by walking around the workplace and looking for anything that could cause harm.
Next, decide who might be at risk and how serious the harm could be. Once you’ve done that, put measures in place to control those risks.
Tip: Involve your team in the process. They often notice hazards others don’t, and it helps build a culture of safety.
Common Compliance Mistakes to Avoid
Many employers do the basics but miss important details. One common mistake is forgetting to update risk assessments after a change — like moving equipment or hiring new staff.
Another issue is failing to train staff on their roles in workplace safety. Everyone should know how to report risks and what to do in an emergency.
Tip: Keep training simple and regular. Short, engaging sessions work better than long, one-off courses.
Building a Culture of Workplace Safety
Compliance isn’t just about paperwork. It’s about creating a culture where workplace safety is part of everyday thinking.
Encourage your team to speak up if they see something unsafe. Reward good safety practices. Most importantly, lead by example — if you take safety seriously, your team will too.
Tip: Display safety reminders around the workplace to keep awareness high.
Moving Forward with Confidence
Health and safety compliance doesn’t have to feel overwhelming. With the right support, it can be straightforward and even empowering.
As an employer, your duty is clear: protect your people. That starts with good planning, honest conversations, and regular health and safety risk assessments.
If you’re unsure where to begin, we’re here to help. Our friendly, modern approach makes compliance less stressful and more supportive — exactly how it should be.
Need help with your workplace safety?
Get in touch today for our expert advice and practical tips to stay compliant with confidence.

The post H&S Compliance In The Workplace appeared first on OJ Health and Safety.
Asbestos in Homes: What You Need to Know (Renovations) 24 Jun 2025, 9:41 am
Asbestos in Homes: What You Need to Know Before You Renovate
If you’re planning a Renovation or Home Refurbishment, asbestos might not be the first thing on your mind. But it should be. Asbestos is still present in many Residential Homes across the UK. Knowing your duty and understanding the risks is vital before you get started.
What is Asbestos and Why Was it Used?
Asbestos is a group of naturally occurring fibres once praised for being strong, fireproof, and cheap. It was widely used in homes between the 1930s and 1999. You’ll find it in ceiling coatings, floor tiles, pipe lagging, and garage roofs. If undisturbed, asbestos is often safe. But during Renovation, disturbing it can release harmful fibres into the air.
Common Places Asbestos is Found in Homes
Most people don’t realise how many parts of their home could contain asbestos. These are the most common spots:
- Artex ceilings and wall coatings
- Insulation board behind fuse boxes and heaters
- Floor tiles and their adhesive
- Cement panels in garage roofs or sheds
- Pipe lagging in older heating systems
These materials were legal to use until 1999. So, any property built or refurbished before that date could contain them.
The Risk During Home Refurbishment
You might be thinking: “I’m just drilling a hole for a light fitting.” Even small tasks can disturb asbestos. During any Renovation or Home Refurbishment, materials are cut, drilled, or removed. This can release dangerous asbestos fibres into your living space.
Exposure can cause serious health issues, including asbestosis and mesothelioma. That’s why identifying asbestos before you begin is a must.
When You Need an Asbestos Survey
Before doing any intrusive work, get an Asbestos Survey. This is especially important in Residential Homes built before 2000. A survey helps you locate any asbestos-containing materials (ACMs) and advises how to manage them.
If you’re a landlord or employer, this is more than just good advice. You have legal employer duties under workplace safety regulations. Even in a domestic setting, if someone is working in your home, you may have a duty to ensure their safety.
Why It’s Not Just About You
Hiring a contractor to help with your Renovation? It’s important to understand who holds responsibility under health and safety law. While you might be the homeowner, legal duties don’t just disappear. Under the Construction (Design and Management) Regulations 2015, your employer duties as a domestic client are usually passed to the contractor or principal contractor. This means they’re legally responsible for managing risks — including asbestos.
However, you still have a duty to make sure the work is carried out safely. Always ask if an asbestos survey has been completed before starting any home refurbishment. It’s a simple tip that could protect lives.
What To Do If You Suspect Asbestos
Don’t panic. The key is not to disturb it. Contact a competent health and safety professional. A proper Asbestos Survey will tell you what you’re dealing with. In many cases, asbestos can be safely managed in place.

Final Tip: Don’t Cut Corners
Skipping an Asbestos Survey to save time or money is never worth it. It could cost you much more in the long run. Protect your family, workers, and future home buyers.
If you’re planning a Home Refurbishment or Renovation, take the safe route. Book an Asbestos Survey and get peace of mind before you start.
Need help? Our friendly and supportive team is here to guide you. Get in touch for expert advice today.
The post Asbestos in Homes: What You Need to Know (Renovations) appeared first on OJ Health and Safety.
Scorching Days Need Cool-Headed First Aiders 18 Jun 2025, 10:29 am
When the sun comes out, so do the risks. Blistering weather can turn every day into multiple health and safety challenges, so staying cool in the heat—especially at work, is vitally important. That’s why having trained first aid support on hand is more than just a good idea. It’s a vital part of your employer duties and overall workplace safety.
Why hot weather changes everything
In cooler months, the risks may be easier to manage. But in summer, even everyday tasks can become hazardous. The heat can lead to dehydration, heat exhaustion, and heatstroke—all serious conditions that require fast, effective first aid.
For outdoor workers, construction teams, or anyone in warm indoor environments, hot weather makes health emergencies more likely. And when emergencies happen, having a calm, confident first aider nearby could be the difference between quick recovery and serious harm.
First aid in the heat: a must, not a maybe
Every employer has a duty to protect their staff. That includes preparing for seasonal risks. In the summer months, that means ensuring you have enough first aid cover to deal with weather-related incidents.
Training is key here. It’s not enough to have someone with a plaster. Your first aiders need to know how to spot the signs of heat-related illness—and what to do when those signs appear. Effective training gives them the confidence to act quickly and correctly, keeping your people safe.

What the law says
UK employer duties under the Health and Safety (First-Aid) Regulations 1981 are clear. You must provide appropriate first aid equipment, facilities, and personnel. This doesn’t change when the sun is shining—in fact, it becomes even more important.
You must also consider training. Regular updates ensure your team is ready for summer-specific risks. This isn’t just about ticking boxes. It’s about showing your staff that their wellbeing is your priority.
Don’t let hot weather catch you out
The summer months might feel relaxed—but heat can create serious pressure. From dizzy spells to heatstroke, hot weather can affect anyone, even the fittest staff.
So, what can you do? Start with a risk assessment. Think about the tasks your team carries out and how heat might make them more dangerous. Then, make sure you’ve got the right number of first aiders, all with up-to-date training.
Encourage your team to take heat seriously. Remind them to stay hydrated, wear sun protection, and take regular breaks in shaded areas.
Staying cool in the heat
Workplace safety is everyone’s responsibility, but it starts with you. As an employer, your duty is to prepare, prevent, and protect.
Having confident, cool-headed first aiders in your workplace isn’t just about compliance. It’s about creating a culture where people feel supported—no matter the temperature.
Whether you’re managing a building site, a retail outlet, or an office with poor airflow, staying cool in the heat is essential. It shows your team that their health matters. It proves your business is built on care, not just compliance.
The post Scorching Days Need Cool-Headed First Aiders appeared first on OJ Health and Safety.
Project Manager: What they are and why they are needed. 12 Jun 2025, 10:00 am
What Is a Project Manager and Why They Are Needed
In today’s competitive environment, having a skilled Project Manager is vital—especially in high-risk industries like health and safety. From managing compliance to coordinating contractors, Project Managers ensure your projects run smoothly, safely, and within budget.
At OJ Health and Safety, we understand the critical role Project Managers play in delivering successful outcomes that meet both client expectations and legal obligations.
What Does a Project Manager Do?
A Project Manager plans, leads, and delivers projects from start to finish. Their role is to:
- Define project goals and scope
- Allocate resources and assign responsibilities
- Manage risk, cost, and time constraints
- Monitor progress and communicate with stakeholders
- Ensure compliance with safety and legal standards
In health and safety, this could involve managing:
- Construction projects under CDM 2015
- Fire safety system upgrades
- Asbestos removal and air monitoring
- Staff health and safety training rollout
Our experienced team at OJ Health and Safety delivers all of these services with qualified Project Managers at the helm.

Why Are Project Managers So Important?
Without clear leadership, even simple projects can go off track. A Project Manager provides:
- Clear direction and accountability
- Efficient use of time and resources
- Risk identification and mitigation
- A single point of contact for clients and stakeholders
In regulated industries like construction or facilities management, the consequences of poor project delivery can be severe. Missed deadlines, safety violations, or budget overruns can have legal and financial implications.
What Is PRINCE2?
PRINCE2 (PRojects IN Controlled Environments) is a structured project management methodology widely recognised across the UK and globally. A PRINCE2-certified Project Manager uses defined processes and principles to ensure that each project is delivered with consistency, control, and measurable results.
Key benefits of PRINCE2:
- Scalable and flexible for any project size
- Clear project governance and defined roles
- Focus on business justification and stakeholder engagement
- Stage-by-stage planning and control
At OJ Health and Safety, many of our project leads hold PRINCE2 certification, ensuring industry best practice is followed at every step.
Why Choose a Health and Safety Project Manager?
By working with a specialist like OJ Health and Safety, you get more than just project coordination—you get health and safety expertise embedded in every decision.
Our Project Managers:
- Understand the legal and regulatory landscape
- Are trained in CDM, fire safety, asbestos compliance and more
- Hold relevant qualifications including PRINCE2, NEBOSH, and IOSH
- Work closely with clients to deliver safe, compliant, and successful projects
Whether you’re overseeing a major refurbishment, managing site safety, or rolling out training across multiple locations, our team will ensure every step is executed with professionalism and care.
Ready to Get Started?
If you’re planning a project that involves compliance, construction, or safety—don’t risk going it alone. Bring in a certified Project Manager from a trusted health and safety partner.
Contact the team at OJ Health and Safety to find out how we can support your next project.
The post Project Manager: What they are and why they are needed. appeared first on OJ Health and Safety.
Energy Efficiency: What Every Property Owner Must Know 4 Jun 2025, 10:32 am
If you’re an employer, landlord, or business owner, you’ve likely heard of an Energy Performance Certificate – or EPC. But do you really know what it is, why it matters, and what your duty is when it comes to getting one?
Let’s break it down in a simple, friendly way – with no jargon and no stress.
What Is an EPC Survey?
An Energy Performance Certificate shows how energy efficient a building is. It gives your property a rating from A (very efficient) to G (inefficient).
The better the rating, the lower your energy bills – and the better your impact on the environment.
You’ll need an EPC if you’re selling, letting, or building a property. This includes commercial premises like offices, shops, and warehouses.
Who Needs an EPC – and Why?
If you’re a landlord or employer, an EPC isn’t optional. It’s a legal duty.
You must make sure your property meets the minimum energy efficiency standards (currently an E rating or better). Failing to do this could lead to fines of up to £5,000.
It’s not just about ticking a box. It’s about protecting your business, reducing energy use, and doing the right thing for people and planet.
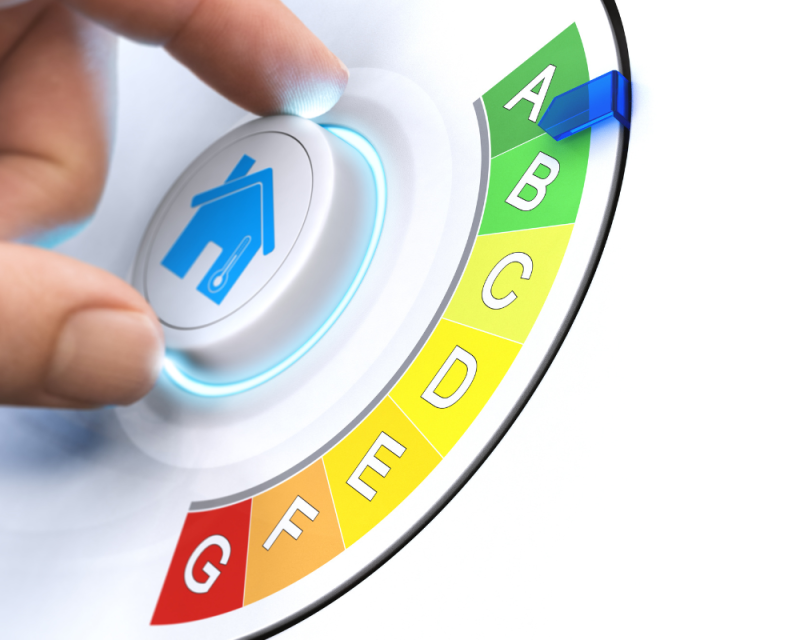

Why Energy Efficiency Matters for Workplace Safety
At first glance, you might not connect EPCs with workplace safety. But they’re closely linked.
An energy-efficient building often means better heating, ventilation, and lighting. That can improve comfort, reduce health risks, and create a safer, more productive workplace.
As an employer, it’s part of your duty to maintain a safe and suitable working environment. Getting an EPC survey helps you identify improvements that benefit your people and your bottom line.
Top Tips for Getting Your Energy Efficiency Right
Getting an EPC doesn’t have to be stressful. Here’s a quick tip: use an accredited assessor who understands your type of building. This ensures your report is accurate and useful.
Another tip: take action on the recommendations in the report. Even small upgrades – like better insulation or energy-saving lighting – can boost your rating and cut costs.
And finally, keep your EPC up to date. It’s valid for 10 years, but if you’ve made changes to your property, you might need a new one sooner.
We’re Here to Help
At OJ Health and Safety, we’re not just about rules and regulations. We’re here to support you, whatever stage you’re at.
Whether you’re a landlord, employer, or managing multiple sites, we’ll help you understand your responsibilities and stay compliant – without the confusion.
From EPC surveys to workplace safety, we bring a modern, friendly approach that puts your needs first.
Need an EPC Survey? Let’s Talk
If you’re unsure whether your property needs an energy performance certificate, or if you’re ready to book a survey, get in touch with our team.
We’ll guide you through the process and make it simple – just as it should be.
The post Energy Efficiency: What Every Property Owner Must Know appeared first on OJ Health and Safety.
Legionella Risk Assessments: All You Need to Know 22 May 2025, 7:42 am
What is a Legionella Risk Assessment?
Do Employers Need a Legionella Risk Assessment?

What Should a Legionella Risk Assessment Include?
-
A description of your water systems
-
Identification of potential risk areas
-
Details of who may be at risk
-
An evaluation of control measures
-
Clear recommendations and actions
Who Can Carry Out a Legionella Risk Assessment?
Tips for Managing Legionella Risks Ongoing
-
Keep records of your assessments and actions
-
Flush little-used outlets weekly
-
Monitor water temperatures regularly
-
Clean and disinfect systems as needed
-
Review your risk assessment annually or after system changes
Why It Matters
Need a Hand?
The post Legionella Risk Assessments: All You Need to Know appeared first on OJ Health and Safety.
Fire Compartmentation Surveys: All You Need To Know 21 May 2025, 9:32 am
Fire compartmentation survey is crucial for workplace safety. They help identify gaps that could allow fire to spread. As an employer, it’s your duty to ensure fire safety through regular inspections and maintenance. In this blog, we will explain why fire compartmentation surveys matter. We will also discuss employer duties and share helpful tips.
What Are Fire Compartmentation Surveys?
Fire compartmentation surveys assess the effectiveness of fire barriers within a building. These barriers include walls, floors, and doors that prevent the spread of fire. The survey identifies any breaches or defects that could compromise fire safety. Employers have a duty to ensure that these barriers are intact and effective.
Why Are These Surveys Important?
Effective fire compartmentation helps contain fires and protect lives. Employers must ensure that fire barriers are properly maintained. A survey highlights any damage or gaps that could allow smoke or flames to pass through. Addressing these issues is a key part of workplace safety and compliance.
Employer Duties Regarding Compartmentation
Employers are responsible for conducting regular fire compartmentation surveys. They must also arrange repairs if defects are identified. Keeping accurate records of inspections and maintenance shows compliance with fire safety regulations. Neglecting this duty can lead to increased fire risks and legal consequences.
How Often Should Surveys Be Conducted?
Surveys should be carried out periodically, especially after refurbishment works. Major changes to the building structure may affect fire barriers. As an employer, regular checks help ensure your duty to maintain fire safety is met.
What Does a Survey Involve?
A fire compartmentation survey involves:
- Inspecting walls, doors, and ceilings for gaps or damage.
- Checking fire-stopping materials and seals.
- Ensuring that fire doors close and latch correctly.
- Identifying any unsealed service penetrations.
After the fire compartmentation survey, a report will outline any issues and recommend corrective actions. Acting on these findings helps you maintain workplace safety.
Maintenance Tips for Employers
To keep fire barriers effective, follow these tips:
- Conduct visual checks for damage after any building work.
- Train staff in staff to spot signs of damage to fire doors and walls.
- Keep records of all surveys and maintenance activities.
By taking a proactive approach, you demonstrate your commitment to safety. It also ensures that fire safety measures are consistently effective.
Final Thoughts
Fire compartmentation surveys are essential for maintaining fire safety in the workplace. Employers have a duty to conduct these surveys and act on any issues found. Regular checks help protect your premises and keep staff safe. For professional advice or to arrange a survey, contact OJ Health and Safety. We’re here to support your compliance needs.

The post Fire Compartmentation Surveys: All You Need To Know appeared first on OJ Health and Safety.
Fire Risk Assessments: All You Need To Know 13 May 2025, 4:46 am
As a fire risk assessor, I think fire risk assessments are absolutely one of the most important aspects of workplace safety. Employers have a duty to ensure that fire safety measures are effective and up to date. In this blog, I will share my thoughts on why fire risk assessments matter. I’ll also give some tips based on my experience.

Why Fire Risk Assessments Are Important
In my opinion, a fire risk assessment is essential because it identifies potential hazards and helps reduce fire risks. I’ve seen many workplaces where a thorough assessment has significantly improved safety. Employers have a duty to carry out these assessments regularly. This ensures that any changes or new risks are promptly addressed.
What Should a Fire Risk Assessment Include?
I would recommend that every fire risk assessment covers the following areas:
- Identifying fire hazards, such as combustible materials or faulty wiring.
- Determining who might be at risk, including staff and visitors.
- Evaluating the effectiveness of current fire safety measures.
- Recording findings and creating an action plan.
- Regularly reviewing and updating the assessment.
- Involve specific fire risk assessment guidance.
Employers have a duty to act on the findings of these assessments. Ignoring issues can put lives at risk and breach fire safety regulations.
My Top Tips for Effective Fire Risk Assessments
Based on my experience, here are a few tips:
- Involve your team: I think involving employees in the assessment process is beneficial. They often notice things that managers miss.
- Be thorough: I’ve previously seen assessments that overlook small but crucial details, like blocked fire exits.
- Update regularly: In my opinion, assessments should be reviewed at least annually, or sooner if changes occur.
- Keep updated with fire risk assessment guidance.
Employer Duties Regarding Fire Risk Assessments
Employers are legally required to conduct fire risk assessments. They must also ensure that staff are aware of fire safety procedures. I’ve seen instances where a lack of training led to confusion during drills. Training is a vital part of maintaining workplace safety.
Common Mistakes I’ve Seen
I have previously seen employers assume that one assessment is enough. Fire safety is an ongoing duty. Risk factors can change, so assessments should be part of routine maintenance. I would recommend scheduling regular reviews and keeping clear records of updates.
Final Thoughts
Fire risk assessments are a key part of workplace safety. As a fire risk assessor, I believe that proactive planning makes a huge difference. Employers have a duty to keep their teams safe by conducting thorough assessments. If you need help or advice, I would recommend speaking with a professional. At OJ Health and Safety, we’re here to support you with reliable fire safety advice.
The post Fire Risk Assessments: All You Need To Know appeared first on OJ Health and Safety.
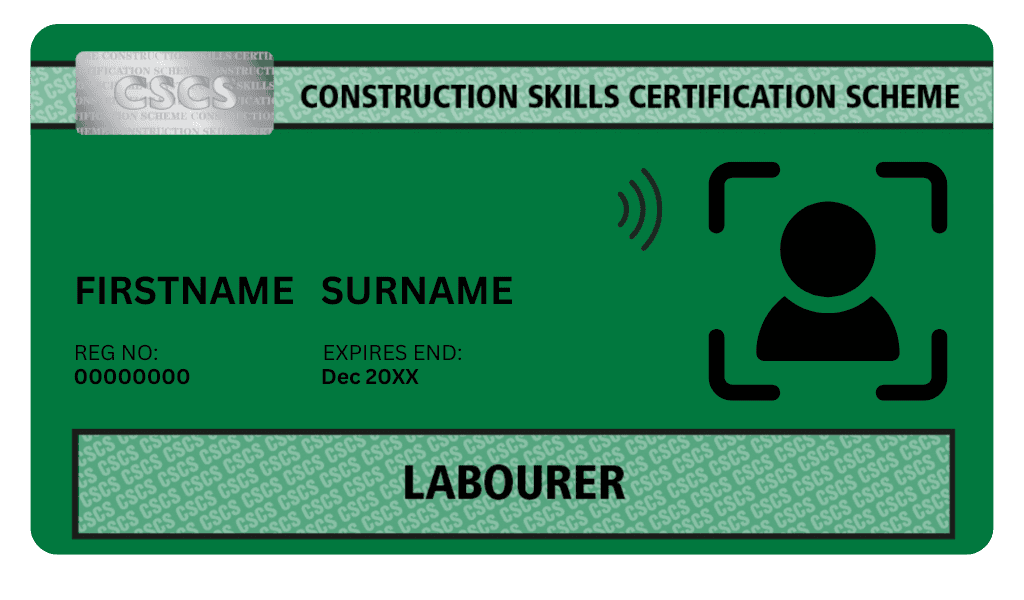
CSCS Cards. Why you need them and what we do. 2 May 2025, 3:45 am
What is a CSCS Card?
CSCS Cards. Why do you need one? The CSCS card (Construction Skills Certification Scheme) is a proof of your qualifications and training for working safely on construction sites in the UK. It shows employers that you have the skills, knowledge, and health & safety awareness to carry out your job properly and safely. You can find more out on https://www.cscs.uk.com/
Why Is It Important?
While not a legal requirement, most major contractors and construction sites require workers to have a valid CSCS card to gain access. It helps raise standards and reduce the risk of accidents on site.
Your Local test centre in Wakefield
We’re proud to offer the services of our brand-new CSCS Test Centre, now open and serving the Wakefield area. Whether you’re just beginning your career in construction or looking to renew your qualifications, our centre offers a professional, convenient, and accessible environment to complete your CSCS test. Just press here to book! https://ojhealthandsafety.co.uk/cscs-card/
What Is the CSCS Test?
The Construction Skills Certification Scheme (CSCS) test—also known as the Health, Safety and Environment (HS&E) Test—is a key requirement for working on most construction sites across the UK. It confirms that workers understand essential health and safety practices, helping to maintain a safe working environment for everyone.
Once you’ve passed the test, you can apply for a CSCS card relevant to your role—whether you’re a labourer, skilled worker, supervisor, or site manager.
Get Your CSCS Card in a Day
In addition to offering the CSCS test, we also provide a CSCS Course + Test Package that allows you to complete the required training and take your test all in one day. This is a perfect solution for anyone who needs to get certified quickly and efficiently.
Our one-day course covers the Level 1 Health and Safety in a Construction Environment qualification, which is required for obtaining a green Labourer CSCS card. After completing the course and passing the test at our centre, you’ll have everything you need to apply for your card without delay.
This fast-track option is ideal for new entrants into the industry or anyone needing their CSCS card urgently.
Why Choose Our Wakefield Test Centre?
Central & Accessible Location – Conveniently located in Wakefield with great transport links.
Nearby Public Parking – Plenty of public parking just a short walk away.
Extended Opening Hours –
Weekdays: 7:00 AM – 7:00 PM
Weekends: 9:00 AM – 3:00 PM
Prices:
CSCS Test: £45.00 + VAT
Full CSCS Course: £170.00 + VAT
Easy Online Booking – Book your test or course quickly through our website.
Friendly Support – Got questions? Our team is happy to help by phone or email.
Whether you’re just starting out or renewing your qualifications, we’re here to help you succeed. With our one-stop solution, you can complete your training and testing in one visit and move forward with confidence.
Book your CSCS course and test today and get everything sorted in just one day—right here in Wakefield.

Key Benefits of sites and workers that use CSCS cards
Improved Health & Safety
Workers with CSCS cards have passed health and safety tests and hold relevant qualifications, reducing the risk of accidents and ensuring safer working environments.
Qualified Workforce
Sites using CSCS cards can be confident that workers are competent and properly trained for their roles, improving the quality of work and project outcomes.
Professional Standards
The CSCS scheme helps promote high standards of professionalism, encouraging responsibility and accountability among workers.
Compliance with Industry Expectations
Many principal contractors and clients require CSCS carded workers as part of their contract terms. Using CSCS cards ensures compliance with these expectations.
Efficient Site Management
When all workers are CSCS carded, site managers can quickly verify credentials and assign tasks more effectively, knowing workers are qualified.
Reputation & Trust
Using CSCS cards builds credibility with clients, contractors, and inspectors by showing a commitment to safe and skilled working practices.

Conclusion
The post CSCS Cards. Why you need them and what we do. appeared first on OJ Health and Safety.
What Is a Health and Safety Retained Service? 28 Feb 2025, 9:14 am
As an employer, ensuring the safety of your workforce is not just a duty, it’s a legal requirement. One way to make sure you are always up to date with health and safety regulations is by using a health and safety retained service. But what exactly does this service offer, and why should you consider it for your business?

What is a Health and Safety Retained Service?
Why Do You Need a Health and Safety Retained Service?

Key Benefits of Health and Safety Retained Services
-
Ongoing Support
Having a retained service means you always have an expert on hand to help with any health and safety concerns. Whether you need assistance with a fire risk assessment or advice on improving your workplace safety, your consultant will be there to guide you. - Compliance with Legal Requirements
As an employer, it’s your responsibility to ensure compliance with health and safety laws, including fire safety regulations. Failure to do so can result in serious consequences. A retained service helps you stay on top of your employer duties, reducing the risk of legal trouble and fines. -
Tailored Risk Assessments
Your retained service provider will conduct regular, thorough risk assessments specific to your workplace. These assessments identify hazards and help you implement the right measures to reduce risks, whether it’s improving fire safety or mitigating other workplace dangers. -
Peace of Mind
Knowing that you have ongoing, expert support can give you peace of mind. Instead of stressing about safety compliance or waiting until an accident happens, you’ll be able to focus on running your business. Your duty of care will be well managed.
How Does It Work?

Conclusion
The post What Is a Health and Safety Retained Service? appeared first on OJ Health and Safety.
Page processed in 4.266 seconds.
Powered by SimplePie 1.3.1, Build 20121030175403. Run the SimplePie Compatibility Test. SimplePie is © 2004–2025, Ryan Parman and Geoffrey Sneddon, and licensed under the BSD License.
